Wild Pointer in C Language with Example Programs

Introduction:
We have looked at the void pointer in c in an earlier article. In today’s article, We will look at the wild pointer in c programming language.
📢 This Program is part of the Pointers Practice Programs series
What is a Wild pointer in C language:
A Wild pointer is a pointer variable, that doesn’t point to a valid memory address. The uninitialized pointer variables are a good example of a Wild pointer in C.
Let’s look at an example of the wild pointer in c language.
|
1 2 |
// declare a pointer int * wPtr; |
Here the wPtr pointer is a wild pointer as we haven’t initialized it with any address.
Accessing Wild Pointer in C:
Accessing the wild pointers will result in undefined behavior. It might introduce bugs in the program and Sometimes the program might crash as well.
|
1 2 |
// undefined behavior, crashes, etc printf("Value pointed by wild pointer is :%d\n", *wPtr); // wPtr is a wild Pointer |
In the above example, We tried to access the value pointed by the wPtr. As the wPtr is a wild pointer, It will result in undefined behavior.
Program to understand the Wild Pointer in C Language – What happens if we access wild pointer:
Here is a program to demonstrate the behavior of the wild pointer and how a wild pointer can cause the program crashes.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
/* program understand the Wild Pointer in C sillycodes.com */ #include<stdio.h> int main() { // create an integer variable int *wPtr; // Try to Access the uninitialized pointer. // undefined behavior, crashes, etc printf("Value pointed by wild pointer is :%d\n", *wPtr); // wPtr is a wild Pointer return 0; } |
In the above program, We have created an integer pointer wPtr and not initialized it. So the wPtr is currently has a garbage value i.e It is pointing to an invalid memory location. Then we tried to print the value pointed by the wild pointer wPtr
Program Output:
Let’s Compile the program.
|
1 |
$ gcc wild-pointer.c |
We used the gcc compiler to compile the program and it generates the a.out executable file.
|
1 2 3 |
$ ./a.out Segmentation fault $ |
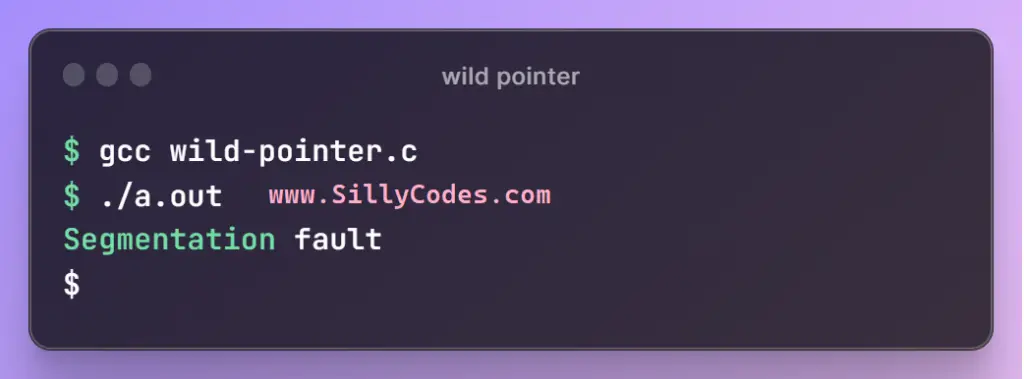
As we can see from the above output, The Dereferencing of the wild pointer wPtr ( *wPtr)caused the Segmentation fault.
The Segmentation fault occurs when you try to access the memory which is not allocated to you. So here the wild pointer wPtr is pointing to some garbage location, So we got the segmentation fault and the program crashed💥.
How to Properly Handle Wild Pointer in C Language?
So it is important to check if the pointer is holding the valid address before trying to dereference the pointer (Access value).
Try to Initialize the pointer variables with appropriate values:
We can initialize the pointer variables with the NULL character instead of simply declaring the value. and check the pointer with NULL before dereferencing the pointer variable.
Initialize the pointer variable with a NULL value.
|
1 2 3 |
// Initialize the pointer int *ptr = NULL; |
While accessing the ptr, check if the ptr is not equal to NULL.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
// check the 'ptr' with NULL. if(ptr != NULL) { printf("value pointed by ptr:%d\n", *ptr); } |
Only access the pointer ptrvalue if contains a valid address of any variable.
Properly Handle Wild Pointer in C – Initialize and Check Pointers before accessing it:
Now, In the following program, We initialized the pointer variable wPtr with the NULL value. While accessing or dereferencing the wild pointer wPtr, We are going to check if the pointer still has the NULL address. If it is still NULL, Then the pointer doesn’t hold any valid address, So we can’t dereference it or use it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
/* program handle wild pointer properly sillycodes.com */ #include<stdio.h> int main() { // Initialize the pointer with NULL int *wPtr = NULL; if(wPtr != NULL) { // print the value printf("Value pointed by wild pointer is :%d\n", *wPtr); // wPtr is a wild Pointer } else { // show warning. printf("Warning: Pointer is Not Initialized!\n"); } return 0; } |
Program Output:
Let’s compile and run the program and observe the output.
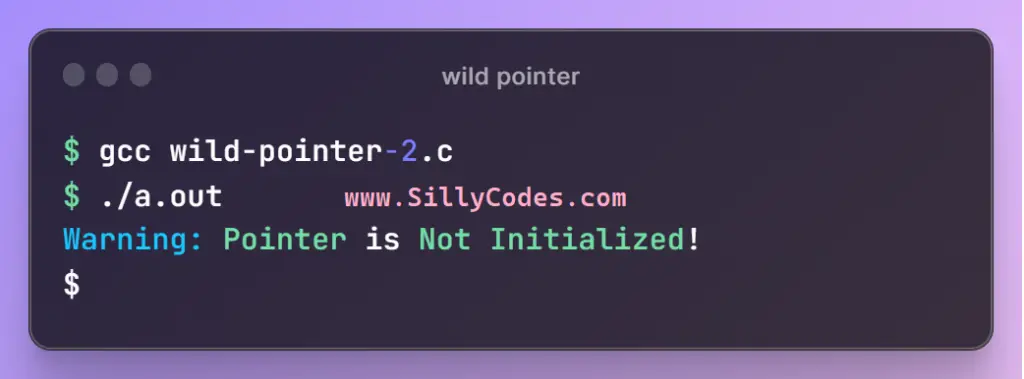
As we can see from the above output, The wild pointer wPtr doesn’t updated and still has the value NULL, We simply printed a warning message Warning: Pointer is Not Initialized!, This way we can avoid program crashes.
If the pointer variable wPtr is indeed updated with the value of a variable, Then the wPtr won’t be equal to the NULL, So the if condition will execute and user gets the proper value.
Related Pointer Programs:
- C Tutorials Index
- C Programs Index – 300+ Programs
- Pointers and Arrays in C Language with Example Programs
- Accessing Array Elements using Pointers in C
- Print String Elements using Pointers in C Language
- Function Returning Pointer in C Programming Language
- Function Pointers in C with Example Programs




1 Response
[…] Wild Pointer in C Language with Example Programs […]